by Marcia L. Anderson and Dr. Changlu Wang
Funded by US EPA
GOT BED BUGS?

Bed bugs are tiny parasites that seek out sleeping people or ani-mals for a blood meal. They are attracted to the CO2 that you exhale, your body heat and your smell. After feeding, they hide. It is extremely challenging, but not impossible, to prevent, detect and control bed bugs.
Protect Yourself From Bed Bugs
The most important step is to learn about bed bugs and prevent them from being introduced. Once bed bugs are found, using Integrated Pest Management (IPM) approach that combines non-chemical and chemical intervention methods provides the best results. IPM relies on knowledge of the pest biology and a combination of multiple methods to eliminate an infestation with minimum cost and impact to the environment and human health.
1. Prevention
- Be aware of where you sit and place your belongings.
- Provide a special place for visitors to place their belongings. Then clean it shortly after they leave.
- Do Not bring second-hand furniture into your home unless you have thoroughly inspected and cleaned the items first.
- Wash bedding regularly.

2. Monitoring
- Visually inspect bed and sofa.
- Place interceptors under bed and sofa legs. Interceptors should be checked every 1-2 weeks. Clean the interior surfaces of the interceptors and reapply talc every 2 weeks to keep the interior surfaces smooth.
3. Environment Modification
- Remove clutter around bed and sofa areas.
- Vacuuming reduces bed bug populations. Immediately seal and dispose of vacuum bags.
- Install encasements on mattress and box spring.
- Make the bed an island: Keep bed away from the wall and do not let bedding touch the floor.
- Install bed bug interceptors under bed and furniture legs.
- Keep clothing off of the floor.
- Isolate infested items in sealed plastic bags or containers.
- Seal cracks where bed bugs can hide.
- If you live in an apartment or other multi-family dwelling, and you see a bed bug, contact your landlord immediately.





Proactive monitoring, early detection, and prompt response will avoid larger problems.
4. Non-Chemical Controls

- Launder bed sheets and clothing regularly.
- Place items in a household freezer for 4 days.
- Dispose of heavily infested items.
- Apply hot steam to infested furniture.
- Place non-washable items in portable heat chambers.
- Other methods available to professionals: whole house heat treatment, containerized heat treatment.
5. Insecticide treatments

- Over the counter insecticide sprays are only effective when sprayed directly on bed bugs.
- Insect foggers are not effective for controlling bed bugs.
- Applying Diatomaceous Earth (DE) dust thoroughly is usually more effective than applying insect sprays for controlling bed bugs. Apply a thin layer of DE to cracks and crevices in walls, bed frames, spaces around the bed, sofa seams, behind wall plates and along junction of wall and floor.
6. Follow up monitoring and treatments
- Monitor bed bug numbers following step 2 regularly. Repeat the above treatments if necessary.
What Do Bed Bugs Look Like?
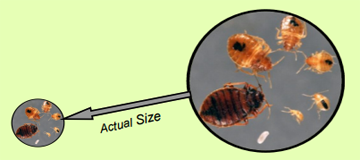
- Adults are rusty red, and apple seed sized, <1/4”, with six legs, oval, and flattened from top to bottom.
- They do not jump or fly, but are good runners and hitch hikers.
- They tend to congregate together.
- The eggs are tiny, white, and glued to surfaces and nymphs are light colored, and 1/16th”.
- Bed bugs can live several months without a blood meal.
Signs of Bed Bugs

- Infestations will leave shed skins, and black and rusty spots on bed linens which are droppings and blood stains from crushed bugs.
- You may have red, itchy welts or rashes from bites; however, bite marks alone are not a reliable indication of a bed bug infestation, as bites could be from any number of other sources.
Be Sure Your Pests are Bed Bugs!!
- Capture and contain several examples of the pest and have them identified by a qualified expert before taking any further actions.
- Skipping this step could be an expensive mistake. Many people have been treated for bed bugs without actually having them.
Recognizing and Finding Bed Bugs

Bed Bug Hiding Places
- Most common places:
- Blankets, bed sheets and pillows.
- Mattresses: along seams and piping, under handles and labels.
- In bed frames and head boards.
- Box springs: under the thin dust cloth, on bottom hidden in nail holes, cracks, by staples, springs and nails.
- Seams and folds of chairs and sofas.
- Less common places:
- Under and along edges of wall-to-wall carpeting and padding.
- Cracks, crevices or nail holes in walls, and under wood moldings.
- Under loose wallpaper and seams.
- In and behind picture frames and mirrors.
- In clothing and clutter stored under beds, in closets and elsewhere.
- Inside switch plates, electrical outlets, and clutter around sleeping areas.
Be alert, Be aware, Bed bugs could be anywhere!
For more information on bed bugs and IPM go to:
www.epa.gov/bedbugs
njaes.rutgers.edu/bedbug/

